Over the past few years, augmented reality apps such as Pokemon Go and Snapchat filters have propelled augmented reality into the mainstream. But while many were seeking out cute creatures, the potential of AR technology has been increasingly recognised across a broad range of sectors and adopted by businesses and organisations to transform our personal and professional lives for good. But what is augmented reality and how does it work in practice?

What is Augmented Reality?
Augmented reality (AR) gives the illusion that real and digital worlds exist in the same space. Augmented reality technology does this by overlaying computer generated content to enhance the real world. Content is limited only by the imagination and can take many shapes and forms, from flat 2D images through to complex and ‘real’ 3D. It’s not just a visual medium; eye catching visual content can be coupled with additional sensory technology, including haptic and auditory.
How Does AR Work?
AR content is usually accessed via a smartphone, tablet or an AR wearable such as the Microsoft Hololens 2. The camera is the key to all AR experiences as it helps users to see digital content in relation to what they are looking at in the real world. It also ensures that devices and apps can collect and process key data, such as location and distance from physical objects to create a seamless experience.
Choosing the right approach to AR content
There are various types of AR content that are designed to work in real world settings in different ways. Choosing which approach to take will depend on the aims and objectives of creating an AR experience.
Marked based
This method requires the user to scan a marked object, or QR code (or something similar) to unlock augmented content. This approach is useful for those looking to create customisable digital twins of objects, such as a car, where users might want to play around with exterior colour options, interior design & dashboard functionality to create their ideal vehicle.
Markerless or location based
Content is geographically-specific, so this approach is great for giving users more information about where they are. It works by using GPS and digital compasses on the user’s phone and can be applied as a wayfinding tool, or providing key information, such as about restaurants and shops in the area.
Superimposition based
This approach gives users the chance to place objects from their screen into their environment; useful for helping to visualise what objects will look like in a specific space. As such, it’s a great tool for furniture retailers as it can help potential customers to see what a piece of furniture will look like in their homes before they buy it.
The Key Differences Between Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality
Immersive technologies take various forms, including augmented, virtual (VR) and mixed reality (MR or XR). But what are the differences between these innovations and how they can be effectively applied to address real life business challenges?
The main distinction between virtual and augmented reality is that AR enhances the world around us, whereas VR offers an escape route to alternative spaces. Virtual reality requires you to don a headset such as HTC VIVE and Facebook’s Oculus Quest to access content that totally blocks out the real world, whereas augmented reality blurs the lines of what is real by accessing content via smartphones, tablets or AR wearable tech such as the Hololens 2.
Virtual and augmented worlds can, and do collide; with mixed reality combining elements of both virtual and augmented reality. Like augmented reality, digital content is laid over the real world in mixed reality. This content is anchored to and interacts with objects in the real world. A major difference between mixed and augmented reality is that in mixed reality, digital assets can be visibly obscured by real world objects.
As with all technologies, choosing the right immersive innovation to address business challenges and opportunities is crucial. For example, sometimes creating a totally virtual space is the driving force, such as creating collaborative working environments for remote teams. In this instance, VR is the ideal choice. From a business perspective, AR’s strengths lie in its key function in blending digital and real worlds – as well as its accessibility to mass markets.
Augmented Reality Applications
Augmented reality in business is already making a tangible difference to the way we live and work. Sectors and businesses leading the way in AR adoption include:
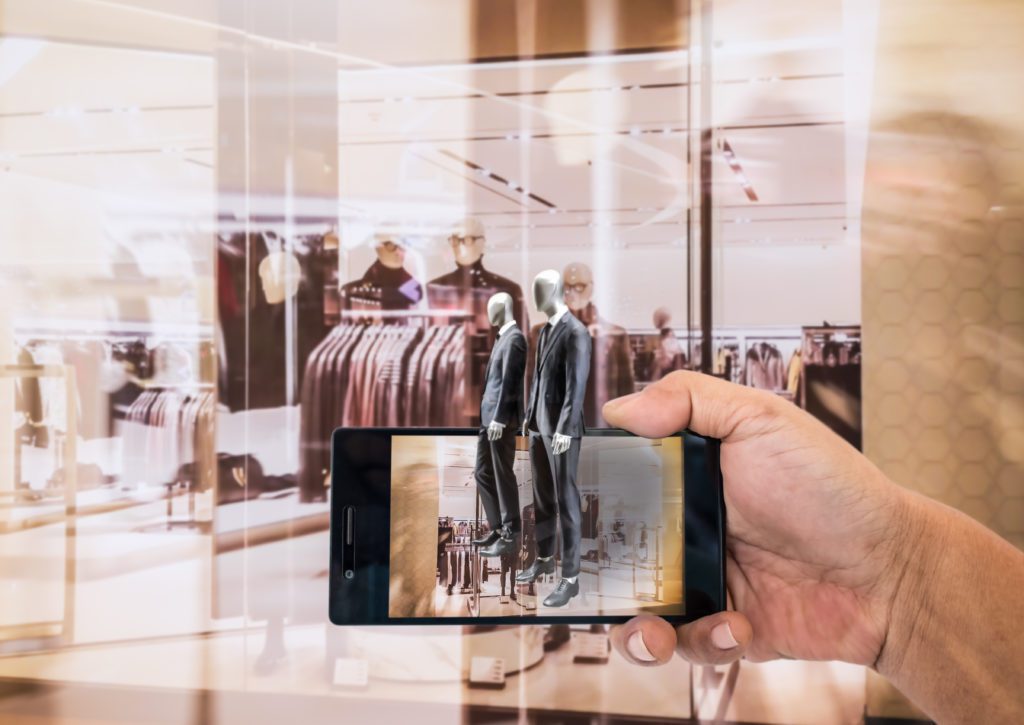

Retail and e-commerce
Augmented reality and retail are a match made in heaven. AR has the power to transform the retail sector by providing an effective “try before you buy” approach which can help to increase customer engagement, raise brand awareness and loyalty, in addition to creating potential new revenue streams.
Furniture buying
Augmented reality can help to take the stress out of shopping for furniture items for customers, in addition to supporting the retailer’s drive to increasing online sales, where customer adoption has traditionally been slow. Customers can find it difficult to visualise exactly how items will fit in with their existing décor, especially when buying online, where there is an additional barrier of being unable to see items in real life.
Retailers such as Ikea and Wayfair have introduced AR apps to give customers a practical tool to help them make purchasing decisions. With the help of smartphones, these apps help to take out the guesswork by transporting 3D models of furniture pieces directly into a customer’s home, where they can place items in different places and walk around to see what items look like from different angles. Crucially for online purchases, customers can get an up-close look at fabrics and finishes.
Fashion retail
The potential impact of AR across the retail sector isn’t simply limited to physical products. In the competitive world of retail fashion, AR isn’t simply a tool for selecting and buying clothes, but replacing them entirely!
New revenue streams are opening up for companies who are innovating in the fashion world by creating AR clothing. In the age of fast fashion, clothing is often bought to be worn once for the creation of social media content, so in effect, physical versions of garments are surplus to requirements in a digital age. Brands such as Tribute and Carlings are producing and distributing AR clothing collections that can be digitally manipulated to fit the wearer in their online images. To maintain a designer feel, the number of collection pieces are limited, but customers benefit from exclusive clothing at a fraction of the cost. Given the significant impact that fast fashion has on the environment, AR fashion also has a place in helping to tackle our climate emergency.

Manufacturing and engineering
Augmented reality can significantly increase productivity by supporting employees to carry out tasks more efficiently and safely, and with fewer errors.
Improving process-driven performance
Augmented reality is ideal for supporting process-driven roles, taking traditional user manuals to a whole new level. By replacing 2D images and text-based instructions, AR can move instructional information into easily accessible 3D guides.
Boeing’s AR training programme highlights the impact that this can have on productivity and quality of work in complex aircraft manufacturing procedures. In a study where AR was used to guide trainees to assemble an aircraft wing section involving 50 steps and 30 parts, trainees were able to complete the task in 35% less time, compared with those using traditional guides. Moreover, the number of trainees with little or no experience who could perform the operation correctly the first time increased by 90%.
Supporting field technicians
As AR can provide a comprehensive and mobile user guide, it is a potential gamechanger for field technicians. As they can draw upon expert help for tailored step-by-step guidance, regardless of where they may be in the world, technicians can solve problems with more speed and accuracy. Having a hands-free kit, such as a Hololens 2 also means that technicians are literally physically freed up to carry out tasks, without having to pause and refer back to manual instructions.
This approach can help to improve performance and reduce costs. When Lee Company, which sells and services buildings systems, introduced AR to help field technicians with installations and repairs, savings of over $500 per technician per month was noted, as having immediate expert advice meant that repeat visits were significantly reduced.
Healthcare
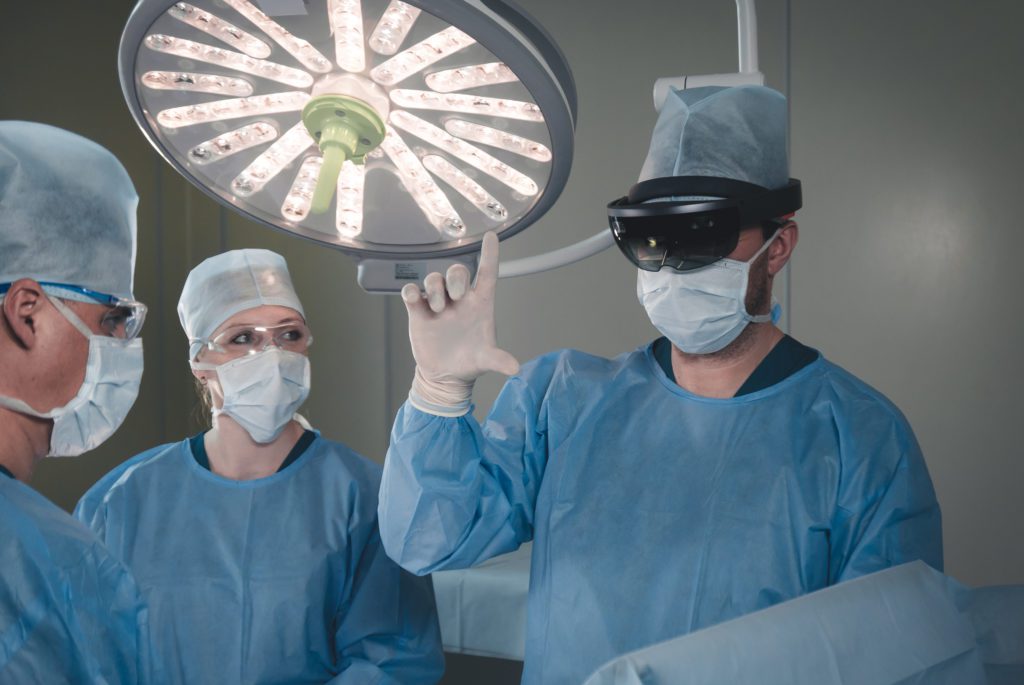
The potential of augmented and mixed reality is increasingly being recognised across the healthcare sector – from becoming an integral part of surgical procedures, through to helping to train medical students and work as a communications tool with patients.
In 2020, this has proven to be a crucial advance for medical teams treating Covid patients, as it has contributed to minimising the risk of transmission to practitioners and patients alike.
Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust hospitals in London introduced Microsoft HoloLens 2 headsets for frontline staff to support them in carrying out their work in treating Covid patients. By combining the HoloLens with Dynamics 365 Remote Assist, a live video stream was fed to a nearby room, where a larger team of clinicians were able to see, as well as advise on everything the doctor was seeing and doing, but from a safe distance. By significantly limiting the number of people needed to be in direct contact with Covid patients, AR had a tangible impact on protecting healthcare workers and patients, lowering the amount of time clinicians need to spend in high risk areas and reducing the amount of PPE needed.
This innovative approach to patient care in a Covid age is also providing a blueprint to changing the way that medical students participate on ward rounds as part of their training and education. As the pandemic has meant that medical students cannot have face-to-face access to patients, St Mary’s Hospital (part of Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust) has started to trial virtual ward rounds. In many ways, this augmented experience allows students to get closer to the patient compared with a usual ward round, as well as giving them instant access to support materials, such as X-rays. Head of the School of Medicine at Imperial, Dr Amir Sam, also believes that this approach can be positive for patients too, who can feel uncomfortable being examined by large groups of medics.
There’s also the benefit that virtual ward rounds can be recorded, giving university hospitals the chance to create libraries of cases and giving more students the chance to see patients with rare conditions and build up their knowledge in how to recognise symptoms and react appropriately.
Live Events
Whether it’s a performance-led or sporting event, corporate conference or trade show, augmented reality in events is changing how we meet and connect for business and entertainment.
Product launches and exhibitions
Augmented reality is also being adopted as a way to stand out from the crowd when showcasing and launching new products. For exhibition-based AR experiences, customers can explore new products in an engaging way that can be individually customised. Moreover, AR can help brands to connect with customers beyond the physical event realm by connecting to further information and websites, which in turn can streamline engagement and purchase processes.
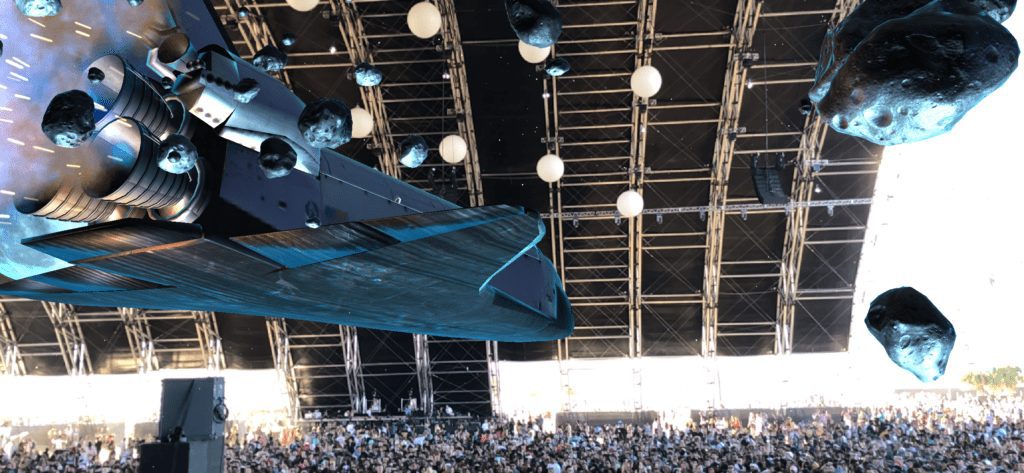

Enhancing attendee experiences
Augmented reality can be applied for practical and creative event planning to make event experiences more enjoyable, accessible and personalised for attendees. For example, at Coachella Festival in 2019, AR was placed centre stage in the Sahara Tent. Concert goers were able to enhance performances by accessing fanciful AR content such as planetary objects, astronauts, space stations and beyond via the Coachella app on their smartphones.
Beyond the enhancement of on-stage activity, AR can offer practical help at events, such as wayfinding tools to add to attendee experience. It can also offer creative ways to expand sponsorship opportunities by providing ways to link attendees to physical spaces and brands.
Benefits of Augmented Reality
In embracing augmented reality into their operational strategies, businesses are able to make workplaces safer and more productive, improve marketing and communications activity to connect with customers, and create new business opportunities.
Augmented reality’s true strength lies in its power to connect and engage with people through the creation of both practical and functional, as well as mind-blowing and imaginative content. By doing this, it has the potential to revolutionise how we live, work, learn, shop and have fun both now and in the years to come.
To find out more about how Future Visual can help to introduce immersive technology solutions into your company, contact us at https://www.futurevisual.com/visionxr/
Over the past few years, augmented reality apps such as Pokemon Go and Snapchat filters have propelled augmented reality into the mainstream. But while many were seeking out cute creatures, the potential of AR technology has been increasingly recognised across a broad range of sectors and adopted by businesses and organisations to transform our personal and professional lives for good. But what is augmented reality and how does it work in practice?

What is Augmented Reality?
Augmented reality (AR) gives the illusion that real and digital worlds exist in the same space. Augmented reality technology does this by overlaying computer generated content to enhance the real world. Content is limited only by the imagination and can take many shapes and forms, from flat 2D images through to complex and ‘real’ 3D. It’s not just a visual medium; eye catching visual content can be coupled with additional sensory technology, including haptic and auditory.
How Does AR Work?
AR content is usually accessed via a smartphone, tablet or an AR wearable such as the Microsoft Hololens 2. The camera is the key to all AR experiences as it helps users to see digital content in relation to what they are looking at in the real world. It also ensures that devices and apps can collect and process key data, such as location and distance from physical objects to create a seamless experience.
Choosing the right approach to AR content
There are various types of AR content that are designed to work in real world settings in different ways. Choosing which approach to take will depend on the aims and objectives of creating an AR experience.
Marked based
This method requires the user to scan a marked object, or QR code (or something similar) to unlock augmented content. This approach is useful for those looking to create customisable digital twins of objects, such as a car, where users might want to play around with exterior colour options, interior design & dashboard functionality to create their ideal vehicle.
Markerless or location based
Content is geographically-specific, so this approach is great for giving users more information about where they are. It works by using GPS and digital compasses on the user’s phone and can be applied as a wayfinding tool, or providing key information, such as about restaurants and shops in the area.
Superimposition based
This approach gives users the chance to place objects from their screen into their environment; useful for helping to visualise what objects will look like in a specific space. As such, it’s a great tool for furniture retailers as it can help potential customers to see what a piece of furniture will look like in their homes before they buy it.

The Key Differences Between Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality
Immersive technologies take various forms, including augmented, virtual (VR) and mixed reality (MR or XR). But what are the differences between these innovations and how they can be effectively applied to address real life business challenges?
The main distinction between virtual and augmented reality is that AR enhances the world around us, whereas VR offers an escape route to alternative spaces. Virtual reality requires you to don a headset such as HTC VIVE and Facebook’s Oculus Quest to access content that totally blocks out the real world, whereas augmented reality blurs the lines of what is real by accessing content via smartphones, tablets or AR wearable tech such as the Hololens 2.
Virtual and augmented worlds can, and do collide; with mixed reality combining elements of both virtual and augmented reality. Like augmented reality, digital content is laid over the real world in mixed reality. This content is anchored to and interacts with objects in the real world. A major difference between mixed and augmented reality is that in mixed reality, digital assets can be visibly obscured by real world objects.
As with all technologies, choosing the right immersive innovation to address business challenges and opportunities is crucial. For example, sometimes creating a totally virtual space is the driving force, such as creating collaborative working environments for remote teams. In this instance, VR is the ideal choice. From a business perspective, AR’s strengths lie in its key function in blending digital and real worlds – as well as its accessibility to mass markets.
Augmented Reality Applications
Augmented reality in business is already making a tangible difference to the way we live and work. Sectors and businesses leading the way in AR adoption include:

Retail and e-commerce
Augmented reality and retail are a match made in heaven. AR has the power to transform the retail sector by providing an effective “try before you buy” approach which can help to increase customer engagement, raise brand awareness and loyalty, in addition to creating potential new revenue streams.
Furniture buying
Augmented reality can help to take the stress out of shopping for furniture items for customers, in addition to supporting the retailer’s drive to increasing online sales, where customer adoption has traditionally been slow. Customers can find it difficult to visualise exactly how items will fit in with their existing décor, especially when buying online, where there is an additional barrier of being unable to see items in real life.
Retailers such as Ikea and Wayfair have introduced AR apps to give customers a practical tool to help them make purchasing decisions. With the help of smartphones, these apps help to take out the guesswork by transporting 3D models of furniture pieces directly into a customer’s home, where they can place items in different places and walk around to see what items look like from different angles. Crucially for online purchases, customers can get an up-close look at fabrics and finishes.
Fashion retail
The potential impact of AR across the retail sector isn’t simply limited to physical products. In the competitive world of retail fashion, AR isn’t simply a tool for selecting and buying clothes, but replacing them entirely!
New revenue streams are opening up for companies who are innovating in the fashion world by creating AR clothing. In the age of fast fashion, clothing is often bought to be worn once for the creation of social media content, so in effect, physical versions of garments are surplus to requirements in a digital age. Brands such as Tribute and Carlings are producing and distributing AR clothing collections that can be digitally manipulated to fit the wearer in their online images. To maintain a designer feel, the number of collection pieces are limited, but customers benefit from exclusive clothing at a fraction of the cost. Given the significant impact that fast fashion has on the environment, AR fashion also has a place in helping to tackle our climate emergency.

Manufacturing and engineering
Augmented reality can significantly increase productivity by supporting employees to carry out tasks more efficiently and safely, and with fewer errors.
Improving process-driven performance
Augmented reality is ideal for supporting process-driven roles, taking traditional user manuals to a whole new level. By replacing 2D images and text-based instructions, AR can move instructional information into easily accessible 3D guides.
Boeing’s AR training programme highlights the impact that this can have on productivity and quality of work in complex aircraft manufacturing procedures. In a study where AR was used to guide trainees to assemble an aircraft wing section involving 50 steps and 30 parts, trainees were able to complete the task in 35% less time, compared with those using traditional guides. Moreover, the number of trainees with little or no experience who could perform the operation correctly the first time increased by 90%.
Supporting field technicians
As AR can provide a comprehensive and mobile user guide, it is a potential gamechanger for field technicians. As they can draw upon expert help for tailored step-by-step guidance, regardless of where they may be in the world, technicians can solve problems with more speed and accuracy. Having a hands-free kit, such as a Hololens 2 also means that technicians are literally physically freed up to carry out tasks, without having to pause and refer back to manual instructions.
This approach can help to improve performance and reduce costs. When Lee Company, which sells and services buildings systems, introduced AR to help field technicians with installations and repairs, savings of over $500 per technician per month was noted, as having immediate expert advice meant that repeat visits were significantly reduced.
Healthcare
The potential of augmented and mixed reality is increasingly being recognised across the healthcare sector – from becoming an integral part of surgical procedures, through to helping to train medical students and work as a communications tool with patients.
In 2020, this has proven to be a crucial advance for medical teams treating Covid patients, as it has contributed to minimising the risk of transmission to practitioners and patients alike.
Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust hospitals in London introduced Microsoft HoloLens 2 headsets for frontline staff to support them in carrying out their work in treating Covid patients. By combining the HoloLens with Dynamics 365 Remote Assist, a live video stream was fed to a nearby room, where a larger team of clinicians were able to see, as well as advise on everything the doctor was seeing and doing, but from a safe distance. By significantly limiting the number of people needed to be in direct contact with Covid patients, AR had a tangible impact on protecting healthcare workers and patients, lowering the amount of time clinicians need to spend in high risk areas and reducing the amount of PPE needed.
This innovative approach to patient care in a Covid age is also providing a blueprint to changing the way that medical students participate on ward rounds as part of their training and education. As the pandemic has meant that medical students cannot have face-to-face access to patients, St Mary’s Hospital (part of Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust) has started to trial virtual ward rounds. In many ways, this augmented experience allows students to get closer to the patient compared with a usual ward round, as well as giving them instant access to support materials, such as X-rays. Head of the School of Medicine at Imperial, Dr Amir Sam, also believes that this approach can be positive for patients too, who can feel uncomfortable being examined by large groups of medics.
There’s also the benefit that virtual ward rounds can be recorded, giving university hospitals the chance to create libraries of cases and giving more students the chance to see patients with rare conditions and build up their knowledge in how to recognise symptoms and react appropriately.
Live Events
Whether it’s a performance-led or sporting event, corporate conference or trade show, augmented reality in events is changing how we meet and connect for business and entertainment.
Product launches and exhibitions
Augmented reality is also being adopted as a way to stand out from the crowd when showcasing and launching new products. For exhibition-based AR experiences, customers can explore new products in an engaging way that can be individually customised. Moreover, AR can help brands to connect with customers beyond the physical event realm by connecting to further information and websites, which in turn can streamline engagement and purchase processes.

Enhancing attendee experiences
Augmented reality can be applied for practical and creative event planning to make event experiences more enjoyable, accessible and personalised for attendees. For example, at Coachella Festival in 2019, AR was placed centre stage in the Sahara Tent. Concert goers were able to enhance performances by accessing fanciful AR content such as planetary objects, astronauts, space stations and beyond via the Coachella app on their smartphones.
Beyond the enhancement of on-stage activity, AR can offer practical help at events, such as wayfinding tools to add to attendee experience. It can also offer creative ways to expand sponsorship opportunities by providing ways to link attendees to physical spaces and brands.
Benefits of Augmented Reality
In embracing augmented reality into their operational strategies, businesses are able to make workplaces safer and more productive, improve marketing and communications activity to connect with customers, and create new business opportunities.
Augmented reality’s true strength lies in its power to connect and engage with people through the creation of both practical and functional, as well as mind-blowing and imaginative content. By doing this, it has the potential to revolutionise how we live, work, learn, shop and have fun both now and in the years to come.
To find out more about how Future Visual can help to introduce immersive technology solutions into your company, contact us at https://www.futurevisual.com/visionxr/